A Conditional Splitting Framework for Efficient Constituency Parsing
Published in ACL 2021 - The 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021
Recommended citation: Thanh-Tung Nguyen, Xuan-Phi Nguyen, Shafiq Joty & Xiaoli Li (2021). A Conditional Splitting Framework for Efficient Constituency Parsing. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Paper Link: not-ready-yet
Abstract
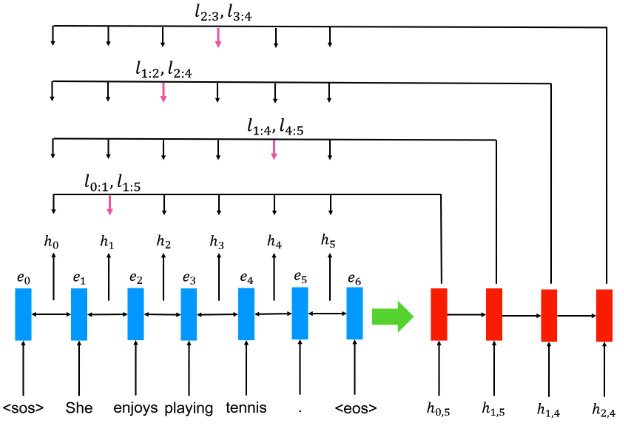
We introduce a generic seq2seq parsing framework that casts constituency parsing problems (syntactic and discourse parsing) into a series of conditional splitting decisions. Our parsing model estimates the conditional probability distribution of possible splitting points in a given text span and supports efficient top-down decoding, which is linear in number of nodes. The conditional splitting formulation together with efficient beam search inference facilitate structural consistency without relying on expensive structured inference. Crucially, for discourse analysis we show that in our formulation, discourse segmentation can be framed as a special case of parsing which allows us to perform discourse parsing without requiring segmentation as a pre-requisite. Experiments show that our model achieves good results on the standard syntactic parsing tasks under settings with/without pre-trained representations and rivals state-of-the-art (SoTA) methods that are more computationally expensive than ours. In discourse parsing, our method outperforms SoTA by a good margin. Our source code will be publicly available.
Summary